Breaking Down the NVDA Stock Split for Investors 2025
Introduction
Nvidia’s rise to the top of the tech world has been nothing short of astonishing. Once known mainly among hardcore gamers and computer engineers for its powerful graphics cards, Nvidia has evolved into a cornerstone of the artificial intelligence revolution. Its market value surged into the trillions, making it one of the most valuable companies on the planet.
In June 2024, Nvidia made headlines again—not because of a new product launch, but because of a corporate action that made waves in the investment world: a 10-for-1 forward stock split. While stock splits are not uncommon, the timing, scale, and symbolic weight of this one caught the attention of analysts, institutional investors, and retail traders alike.
For some, the split was a welcome opportunity to buy into Nvidia at a “more affordable” price. For others, it was an indicator that the company’s leadership is confident in the continued growth of its business. But what does it really mean? To understand the full impact, we need to break down the mechanics of a stock split, Nvidia’s motivations, and how it could affect the market in the short and long term.
What Is a Stock Split?
A stock split is a corporate action where a company increases the number of its outstanding shares while proportionally reducing the price per share. The overall market value of the company remains unchanged—think of it like cutting a pizza into more slices. The total amount of pizza stays the same, but now more people can take a piece.
If you owned one share worth $1,000 and the company performed a 10-for-1 stock split, you would suddenly own ten shares worth $100 each. Your total investment value is still $1,000, but it’s now spread across more shares.
Stock splits can be forward splits (more shares, lower price) or reverse splits (fewer shares, higher price). Forward splits are typically done when a company’s share price climbs so high that it risks becoming psychologically or practically out of reach for smaller investors.
The key point is that a stock split doesn’t change the fundamentals of the company. It’s a cosmetic and logistical change. However, it often has real effects on trading behavior, liquidity, and investor sentiment.
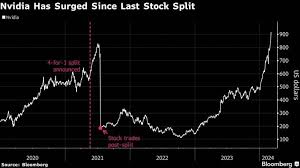
Nvidia’s June 2024 10-for-1 Split
In May 2024, Nvidia announced its 10-for-1 forward stock split, which took effect in early June. Before the split, Nvidia’s shares were trading around $1,200. On the first trading day after the split, the adjusted price was roughly $120.
This was not Nvidia’s first split—far from it. The company has executed multiple splits in its history, usually during periods of rapid growth. But this one stood out because of Nvidia’s size at the time. By the split date, Nvidia had already become one of the world’s most valuable companies, powered by surging demand for AI chips, data center GPUs, and advanced computing solutions.
The split was also paired with a sizable dividend increase, a rare move for a tech company that has historically prioritized reinvestment over cash payouts. This combination sent a strong message to the market: Nvidia was thriving, confident, and willing to share more of its success with shareholders.
Why Nvidia Split Its Stock
So why did Nvidia decide to go through with this split? There are several key reasons:
- Accessibility for Investors
At $1,200 a share, Nvidia’s stock was out of reach for many retail investors—especially those who prefer to buy whole shares rather than fractions. By bringing the price down to the low hundreds, the company made ownership feel more attainable. This psychological factor can attract new investors who might have been hesitant before. - Liquidity Enhancement
A lower share price often translates to higher trading volume. With more people able to buy and sell in smaller increments, the stock becomes more liquid. Higher liquidity means tighter bid-ask spreads and a smoother trading experience for everyone. - Employee Stock Plans
Nvidia rewards its employees with stock-based compensation. A lower share price makes it easier for employees to receive and sell shares in meaningful quantities without dealing with extremely high per-share values. - Signaling Confidence
Stock splits are often interpreted as a sign that a company’s leadership expects the share price to continue rising in the future. Nvidia’s management wouldn’t split the stock if they thought the price was likely to collapse. The timing—right after stellar earnings—reinforced this impression.
Immediate Market Reactions
The announcement of the split sparked immediate excitement. In the days following the news, Nvidia’s stock surged as investors rushed in. Even though a split doesn’t inherently increase a company’s value, the buzz and positive sentiment can drive short-term gains.
Institutional investors welcomed the move, as it opened the door to greater retail participation. Meanwhile, options traders benefited from having contracts priced at lower strike levels, which expanded trading strategies and opportunities.
By the time the split took effect, Nvidia’s momentum was already in full swing. On the first trading day post-split, trading volumes jumped, and the new share price attracted a fresh wave of small-scale investors.
Historical Performance Post-Split
Looking at Nvidia’s history, stock splits have often been followed by periods of strong performance. That said, they’re not a guarantee of continued gains. In some cases, the post-split rally has been followed by a cooling-off period as traders take profits and the initial excitement fades.
Historically, many companies experience a short-term bump after a split due to increased buying activity from retail investors. Over the long term, the stock’s trajectory depends entirely on business fundamentals—revenue growth, profitability, innovation, and market conditions.
For Nvidia, the fundamentals have remained extremely strong. Demand for AI hardware and cloud computing capacity is still surging, and the company continues to dominate the GPU market. These drivers could help sustain the stock’s momentum well beyond the initial split hype.
Implications for Retail and Institutional Investors
For Retail Investors:
The most obvious benefit is the lower price per share, which makes it easier to buy in without committing a large sum upfront. For example, a new investor could purchase a handful of Nvidia shares for a few hundred dollars instead of needing over a thousand dollars for just one share. This increased accessibility can also help investors diversify their portfolios more effectively.
For Institutional Investors:
While large funds and asset managers don’t typically care about nominal share prices, they do benefit from increased liquidity. More shares in circulation can improve the efficiency of large trades and reduce market impact. In addition, a more active options market post-split can create new opportunities for hedging and speculative strategies.
Tax and Accounting Impact
From a tax perspective, a stock split is neutral. You don’t owe taxes simply because the split occurred, and your total cost basis remains the same—though it’s spread across more shares. If you owned one share at a $1,000 cost basis before, after a 10-for-1 split you’d have ten shares with a $100 cost basis each.
For companies, the split requires administrative adjustments but doesn’t alter their financial standing. However, splits can increase investor engagement, which might indirectly influence stock demand and price trends.
Psychological Factors in Stock Splits
Behavioral finance plays a big role in how investors react to stock splits. A lower price can make a stock feel more affordable, even though its intrinsic value hasn’t changed. This “nominal price illusion” often drives buying activity after a split.
In Nvidia’s case, the psychological effect was amplified by the company’s high-profile role in the AI boom. Investors who had been watching from the sidelines suddenly felt they had an easier entry point. Combined with glowing headlines, this helped push demand higher.
Could Nvidia Split Again in the Future?
Given Nvidia’s growth trajectory, another stock split isn’t impossible. If the share price climbs significantly again, management might consider another split to maintain accessibility. That said, companies don’t want to split too often, as it can diminish the perceived significance of the move.
The decision will ultimately depend on future stock performance, market conditions, and Nvidia’s corporate strategy. If demand for AI computing continues at its current pace, another split within a few years would not be surprising.

Risks and Downsides
While stock splits are generally seen as positive, they’re not risk-free:
- Overvaluation Risk: A split can attract speculative traders, pushing the price above fair value.
- Post-Split Declines: After the initial excitement fades, some stocks pull back as traders take profits.
- Misinterpretation: New investors may mistakenly think the split itself creates value, leading to poor investment decisions if they ignore fundamentals.
For Nvidia, the main risk is that investor enthusiasm could run ahead of reality. While the company is fundamentally strong, the market can sometimes overreact in both directions.
Conclusion
Nvidia’s June 2024 stock split was more than just a cosmetic change—it was a strategic move that increased accessibility, boosted liquidity, and signaled confidence in the company’s future. While the split itself doesn’t alter Nvidia’s fundamentals, it has helped broaden the shareholder base and keep the stock in the spotlight.
For investors, the split presents an opportunity to buy into one of the most important tech companies of our time at a more approachable share price. But it’s important to remember that long-term success depends on Nvidia’s continued innovation and execution in the AI and computing space—not on the number of shares in circulation.


